Educator, author and reading expert Laura Robb offers her research-based argument for refocusing American school reform on strategies that will strengthen support for teachers and promote opportunities for children to engage in creative play and become the critical, divergent thinkers we need to solve 21st century problems. Robb recently returned from a month in China visiting schools.
by Laura Robb
Much of the educational reform that comes out of the federal and state departments of education is in response to the results of state testing and two large scale assessments: PISA (Program for International Student Assessment) and the NAEP (National Assessment of Educational Progress).
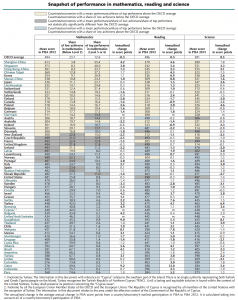
A look at the 2012 PISA scores in reading, as reported by the Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), leads to conclusions that can, and should, alter the direction of educational reform in the United States. But we have to move beyond simply listing the results of countries who score higher than the USA and appealing to our citizens’ nationalist impulses. We need to examine the educational policies of these countries to learn what is and isn’t working well in our public schools.
The National Education Association explains that high-scoring OECD countries invest in early childhood education, fully fund all schools, value the teaching profession and support teachers, and encourage collaboration among parents, administrators, communities, and elected officials. Recent policy trends in the USA appear to be moving in a counter-direction.
Some facts about PISA and the United States
About 510,000 15-year-old students from 34 OECD countries took the 2012 PISA test. The United States ranked 17th in reading. Trend data in reading show no significant changes in the performance of 15-year-olds in the United States since 2000, after a decade of NCLB and related “reforms.” This performance picture appears even more worrisome when factoring in the reading trend scores of nations such as Shanghai-China, Singapore, Korea, Japan, Canada, and Switzerland, where performance continued to rise over the same period of time.
A less visible PISA story has to do with student performance in our schools that serve our most socio-economically challenged students.
Among OECD countries, the U.S. has the highest percentage of poverty: 21.7%, with New Zealand in second place at 16.3%. When we compare schools in the United States in which less than 10% of the students live in poverty to similar samples in other OECD countries, the PISA reading scores tell a dramatically different tale about our students’ reading success: among these non-impoverished populations, the U.S. ranks near the top in reading scores.
In an April 2014 blog post, education historian Diane Ravitch invited education scholar David Berliner to share his research drawing a direct relationship between poverty and students’ performance on the PISA. I believe this relationship extends to the NAEP and state tests as well. Instead of continuing to spend millions of dollars on Common Core and state tests (and diverting funding from materials that support students’ learning, books for libraries, salaries for school librarians, and ongoing professional study for teachers), we should be attacking the problems of poverty and equity.
The poverty factor
As early as the 1960’s, the U.S. Department of Education commissioned James S. Coleman and several other scholars to study equity in American schools. The results of the report were not well received in many parts of the country because the report provided arguments for desegregation. Coleman’s report argued that students’ background and socioeconomic status are more instrumental in determining educational outcomes and therefore, disadvantaged black students would benefit from learning in racially-mixed classrooms.
Around thirty years later, the research of Hart and Risley (1995) showed that the literacy gap between families living in poverty and middle class and professional families starts soon after birth.
Many adults living in poverty are unaware of the benefits of “parentese,” the continual stream of talk to babies that parents in middle class and professional families typically engage in. Author Tina Rosenberg wrote in the New York Times in 2013: “By the time a poor child is one year old, she has most likely already fallen behind middle class children in her ability to talk, understand, and learn.” By age four, children living in poverty have heard only 13 million words while children from middle class and professional families have heard 48 million words.
Since a recent NAEP study has shown a tight correlation between vocabulary and reading comprehension, some of the challenges facing the U.S. today are to greatly reduce the number of families living in poverty, educate all parents and daycare caregivers about the importance of talking to children in meaningful ways from birth on, and bring equity to under-resourced schools.
Poverty and achievement
It’s difficult to comprehend that the U.S., the wealthiest nation in the world, cannot significantly reduce the amount of poverty and raise the achievement levels of all children. Or that federal and state departments of education have failed to factor into their reform policies the significance of our high poverty rate, the lack of equity in education, and the relationship of poverty and inequity to children’s ability to learn and achieve.
Most of the lowest achieving schools in the U.S. have the highest number of disadvantaged students and are under-resourced. Yet, the thinking that is shaping education policy today seems to be that greater accountability, more “rigorous” curriculum standards, and tougher tests are sufficient to produce better teaching, higher test scores and “success for all.” Nowhere is the issue of poverty even acknowledged in current government initiatives.
Certainly the educators who work in state and federal education departments know better – many of them have worked in such communities and schools. But too often, a code of silence prevails in the face of misguided political decisions.
With the professed belief among policy makers and advisors that stricter accountability for teachers and administrators can reverse our downward reading-score trend, a national culture of blame and finger pointing has arisen. States have adopted regressive policies that tie teachers’ and administrators’ evaluations to students’ test scores, possibly affecting job security and punishing schools in high poverty communities by labeling them as “failing.”
Such accountability ignores the fact that every student can make progress, but not every student can meet the one-size-progress-for-all goal set by state departments of education. In this punitive and negative climate, it can become increasingly difficult to find teachers willing to work with English language learners, special education students, and high-poverty populations who can, and do, improve but often don’t meet mandated progress levels.
We admonish teachers to not teach to the test. Yet their evaluations of job performance depend on the annual test scores. So, of course teachers will teach to the tests, even though doing so adversely affects all children’s education by diminishing creative, innovative, and critical thinking.
Suppressing creative and critical thinking
At the College of William and Mary in Virginia, Dr. Kyung Hee Kim, an educational psychologist, started a study of creativity test results in 1990 and published her findings in 2011. Dr. Kim revealed a significant decrease in the creativity scores of children in kindergarten through grade six in the United States.
As Dr. Kim described in the 2012 Torrance Lecture at the University of Georgia College of Education, creativity scores, which had been on the rise prior to 1990 and prior to the No Child Left Behind and Reading First initiatives, have been steadily falling for the past two decades.
Dr. Kim’s study also showed that the relationship between IQ and creativity is small. According to Dr. Kim, creativity requires a climate and attitude where teachers and parents support students to play, explore new ideas, and experience a combination of convergent and divergent thinking.
Creative children can generate a wide range of ideas to solve problems. In particular, divergent thinking is the aspect of creativity that future generations will need to solve problems of war and genocide and fast-spreading diseases like Ebola.
The play and exploration in active learning environments that education philosopher and psychologist John Dewey described more than a century ago mirror the ways that children learn and develop creative, divergent thinking. It’s by doing, by pretending and role-playing, by listening to dozens of books read each day and discussing and dramatizing them, by engaging in meaningful conversations, by collaborative and generative problem solving, painting, dancing, and music, that children develop creativity.
With the onset of state and Common Core tests, our nation has adopted teaching practices that deter creative thinking and innovation. In an effort to improve reading scores, play as a way of exploring and learning has been greatly reduced in preschool. Instead, three- and four-year-olds spend their time learning the alphabet, studying letter-sound relationships and sight words, and developing phonemic awareness skills – in lieu of engaging in play as a way to understand concepts, group and classify items, and problem-solve.
 Likewise, among five-year olds in many kindergartens around the U.S., the amount of learning through play, exploration, and divergent thinking has been diminished and replaced with completing phonics, reading, and spelling worksheets so teachers can lead guided reading groups.
Likewise, among five-year olds in many kindergartens around the U.S., the amount of learning through play, exploration, and divergent thinking has been diminished and replaced with completing phonics, reading, and spelling worksheets so teachers can lead guided reading groups.
In elementary and middle schools, many districts have removed or reduced recess, divergent thinking and problem solving, art, music, and dance to gain more time for drilling sight words and math facts, completing worksheets, and teaching to pacing guides.
While some schools are showing signs of a counter-trend, the shift to a more whole-child learning approach is far too slow, with little open support from high-level decision makers. Across America, children still work, work, work with few breaks to give the mind time to process, understand, connect, and absorb new material.
As long as this practice prevails, we’re failing at a crucial job of education in the 21st century — working to develop students’ collaborative problem solving and inferential and divergent thinking. These skills are necessary to solve global problems that continue to affect life on the earth: diminished water supplies, climate change, and poverty.
Our failure to support our teachers
In all the spirited discussion about educational reform, the role of the teacher as learning leader has been marginalized. And yet, it is teachers who spend most of the day with children and can reverse the downward trend of creativity and critical thinking. If there is one element of education that needs to be re-evaluated today, it’s the way we conceptualize teaching.
In 2002, Richard Allington did a study among fourth grade teachers that indicated that it’s the teacher who makes the difference in students’ learning. (Download Allington’s Kappan report on his findings: “What I’ve Learned About Effective Reading Instruction from a Decade of Studying Exemplary Elementary Classroom Teachers.”)
 More recently, in an Atlantic article titled“Building Better Teachers,” teacher-author Sara Mosle reflects on the strengths and shortcomings found in a recent book about improving teaching by Elizabeth Green, founder of GothamSchools. Mosle then offers her own research-supported ideas for lifting education out of the shadows.
More recently, in an Atlantic article titled“Building Better Teachers,” teacher-author Sara Mosle reflects on the strengths and shortcomings found in a recent book about improving teaching by Elizabeth Green, founder of GothamSchools. Mosle then offers her own research-supported ideas for lifting education out of the shadows.
Mosle notes that American teachers clock 1,051 hours in the classroom annually while high school teachers in Finland clock 553 classroom hours, and those in Japan log only 500 classroom hours a year. In fact, with the exception of Chile, American teachers spend more hours in the classroom than teachers of any country that belongs to the OECD. This comparison underscores the fact that American teachers have little time during the day to collaborate with colleagues about lesson plans and students’ progress.
Mosle also points out that OECD countries with high scores on international reading tests emphasize these key aspects of effective teaching: collaborative lesson planning, conferring with students, mentoring and coaching programs, parent involvement, and individual and collaborative professional study. In top-performing countries, teachers routinely meet with colleagues to discuss research and methods of learning and to provide feedback to each other about students’ progress.
How we can make changes for the better
Studying data from the NAEP and PISA but then continuing on our same educational path and bolstering our blame culture will not reverse declining literacy and creativity scores among American children, especially not those living in poverty.
So, what can create positive change in education in the U.S.? Policy makers need to value and include educational researchers, master teachers, and school administrators as important players in determining educational policy and using best-practice research to accomplish 10 key changes:
- Recognize the role that poverty plays in students’ achievement and work tirelessly to eliminate poverty through education and job training.
- Fund all schools equitably and eliminate disadvantaged and under-resourced schools.
- Make the finest preschools available to every child in the USA – schools where creative play is high valued and supported.
- Develop a curriculum that encourages divergent, innovative thinking to equip future generations to tackle global challenges.
- Educate all parents about the importance of engaging their children in meaningful talk, literacy, and creative, divergent thinking from birth.
- Provide ongoing professional learning opportunities at the building level so teachers can succeed with meeting the needs of diverse populations.
- Provide teachers with mentoring and coaching to help them move from fact-driven, memorized curriculum to curriculum that asks students to think at high levels, collaborate, innovate, and problem-solve.
- Build time into teachers’ schedules for collaboration with colleagues so they can work together to support students’ learning.
- Allocate funds to send teachers to major education conferences to foster professional learning and keep them abreast of the newest research.
- Develop assessment systems that encourage success and growth over blame and failure in order to serve the needs of all children in the U.S.
Write to your state and federal representatives. Rally your colleagues. Numbers count. Let’s start today.
MIDDLEWEB · 10/09/2014
 Laura Robb is co-organizer of The Educator to Educator Foundation(E2E) which strives to provide print and e-books to high poverty school and class libraries from preschool to high school and develop professional libraries for teachers that can help them to prepare problem solvers, expert readers and writers, expert users of technology, collaborators, and creative thinkers. She is a veteran teacher and literacy coach and the author of more than 15 books for teachers, including her latest, Unlocking Complex Texts(Scholastic, 2013).
Laura Robb is co-organizer of The Educator to Educator Foundation(E2E) which strives to provide print and e-books to high poverty school and class libraries from preschool to high school and develop professional libraries for teachers that can help them to prepare problem solvers, expert readers and writers, expert users of technology, collaborators, and creative thinkers. She is a veteran teacher and literacy coach and the author of more than 15 books for teachers, including her latest, Unlocking Complex Texts(Scholastic, 2013).